将Transforming a WordPress Server Dashboard into a Widget

回想一下,所有小部件提供程序都必须实现 Provider 接口。它们还必须位于名为 widget 的文件夹内,并位于名称空间 AX\StatBoard\Widget 下。如果我们想添加一种新的指标,只需创建一个相应的类,并创建一个对象并使用 add_provider 方法将其添加到 Widget 类中。
RAM 使用情况小部件
我们想要显示的第一条信息是当前正在使用的 RAM 量以及当前空闲的 RAM 量。
在本例中,free -m 是我们的朋友 - 它告诉我们 RAM 使用情况。 -m 开关是以兆字节为单位输出结果。
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ free -m
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 589 366 223 0 9 57
-/+ buffers/cache: 299 290
Swap: 0 0 0
我们将类命名为 Ram。相应的文件将为 widget/ram.php。我们在这里只是编写基础并实现 get_title 。
<?php
namespace AX\StatBoard\Widget;
class Ram implements Provider {
function __construct() {
}
public function get_title() {
return "Ram Usage";
}
?>
<?php
function get_metric() {
$df = `free -m | grep -E "(Mem|Swap)" | awk '{print $1, $2, $3, $4}'`;
$df = explode("\n", $df);
if ( is_array( $df ) && 2 <= count( $df ) ) {
$df = array_map( function ( $line ) {
if ( empty( $line ) ) {
return;
}
$segment = preg_split( '/\s+/', $line );
return array(
'type' => trim( $segment[0]," :" ),
'total' => (int)$segment[1],
'used' => (int)$segment[2],
'free' => (int)$segment[3],
);
}, $df );
return $df;
}
return false;
}
?>
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ free -m | grep -E "Mem|Swap" | awk '{print $1, $2, $3, $4}'
Mem: 589 541 47
Swap: 255 0 255
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$
- type:第一个字段
- total:第二个字段
- used:第三个字段
- free:第四个字段
public function get_content() {
$metric = $this->get_metric();
$data = array(
array('Type', 'Used(MB)', 'Free(MB)')
);
foreach ($metric as $item) {
if (empty($item)) {
continue;
}
if ($item['type'] !== 'Mem' && $item['type'] !== 'Swap') {
continue;
}
if ( 0 == ($item['free'] + $item['used'])) {
continue;
}
$data[] = array(
$item['type'],$item['used'], $item['free']
);
}
$data = json_encode($data);
echo <<<EOD
<div id="widget_ram_usage"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
google.setOnLoadCallback(function () {
var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable({$data});
var options = {
isStacked: true
};
var chart = new google.visualization.ColumnChart(document.getElementById('widget_ram_usage'));
chart.draw(data, options);
})
</script>
EOD;
}

安装的软件
我们将介绍的第二个小部件是显示已安装软件的小部件。它是一个小部件,旨在显示我们在服务器上有哪些常见软件包以及哪个版本。
<?php
namespace AX\StatBoard\Widget;
class Software implements Provider {
function __construct() {
}
public function get_title() {
return "Installed Software";
}
function get_metric() {
$cmds = array();
$package = array(
'php' => '-v',
'node' => '-v',
'mysql' => '-V',
'vim' => '--version',
'python' => '-V',
'ruby' => '-v',
'java' => '-version',
'curl' => '-V');
foreach ( $package as $cmd=>$version_query ) {
if ( NULL == $cmds[$cmd] = shell_exec( "which $cmd" ) ) {
$cmds[ $cmd ] = 'Not installed';
continue;
}
$version = shell_exec( "$cmd $version_query" );
$version = explode( "\n", $version );
if ( is_array( $version ) ) {
$version = array_shift( $version );
}
$cmds[ $cmd ] .= '<br>' . $version;
}
return $cmds;
}
public function get_content() {
$cmds = $this->get_metric();
$content = '';
foreach ( $cmds as $cmd => $info ) {
$content .= "<p><strong>$cmd</strong> $info</p>";
}
echo $content;
}

磁盘使用情况
现在我们将解决磁盘使用问题。我们将处理此任务的类命名为 Disk。让我们先制作基本骨架。
<?php
namespace AX\StatBoard\Widget;
class Disk implements Provider {
function __construct() {
}
public function get_title() {
return "Disk Usage";
}
}
<?php
function get_metric() {
$df = `df -h`;
$df = explode("\n", $df);
if (is_array($df) && count($df)>=2) {
array_shift($df); //Get rid the first line
$df = array_map(function ($line) {
if (empty($line)) {
return NULL;
}
$segment=preg_split('/\s+/', $line);
return array(
'filesystem' => $segment[0],
'size' => $segment[1],
'used' => $segment[2],
'available' => $segment[3],
'use_percent' => $segment[4],
);
}, $df);
return $df;
}
return false;
}
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/sda1 7.3G 1.4G 5.6G 20% / tmpfs 295M 0 295M 0% /dev/shm /vagrant 60G 55G 4.9G 92% /vagrant /data/GeoIP 60G 55G 4.9G 92% /data/GeoIP /var/webapps 60G 55G 4.9G 92% /var/webapps /var/www/html 60G 55G 4.9G 92% /var/www/html
public function get_content() {
$metric = $this->get_metric();
$data = array(
array( 'Disk', 'Space' )
);
$disk_container = array();
$data_partition = array(
array('Filesystem', 'Free(GB)', 'Used(GB)')
);
foreach ( $metric as $disk ) {
$size = intval( $disk['size'] );
if ( 'M' == substr( $disk['size'], -1 ) ) {
$size = round( $size / 1024, 2 );
}
$used = intval( $disk['used'] );
if ('M' == substr( $disk['used'], -1 ) ) {
$used = round( $used / 1024, 2 );
}
if ( empty( $size ) ) {
continue;
}
$data[] = array( $disk['filesystem'], $size );
$data_partition[] = array($disk['filesystem'], $size - $used, $used);
}
}
[ ['File System', 'Free', 'Used', ['/dev/sda1', 10, 24], ['/dev/sda2', 28, 19]]
- 第一个图表显示了每个已安装文件系统的总空间。对于此数据,我们将使用饼图。
- 第二个图表用于显示每个已安装文件系统的磁盘使用情况。为此,我们将使用条形图。
为此,我们将方法修改为以下内容:
public function get_content() {
$metric = $this->get_metric();
$data = array(
array('Disk', 'Space')
);
$disk_container = array();
$data_partition = array(
array('Filesystem', 'Free(GB)', 'Used(GB)')
);
foreach ($metric as $disk) {
$size = intval($disk['size']);
if ('M' == substr($disk['size'], -1)) {
$size = round($size / 1024, 2);
}
$used = intval($disk['used']);
if ('M' == substr($disk['used'], -1)) {
$used = round($used / 1024, 2);
}
if (empty($size)) {
continue;
}
$data[] = array($disk['filesystem'], $size);
$data_partition[] = array($disk['filesystem'], $size - $used, $used);
}
$data = json_encode($data);
$data_partition = json_encode($data_partition);
echo <<<EOD
<div id="widget_disk_usage"></div>
<div id="widget_disk_partion"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
google.load("visualization", "1", {packages:["corechart"]});
google.setOnLoadCallback(function () {
var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable({$data});
var options = {
is3D: true,
};
var chart = new google.visualization.PieChart(document.getElementById('widget_disk_usage'));
chart.draw(data, options);
var data2 = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable({$data_partition});
var options2 = {
isStacked: true
};
var chart2 = new google.visualization.ColumnChart(document.getElementById('widget_disk_partion'));
chart2.draw(data2, options2);
})
</script>
EOD;
}
<div id="widget_disk_usage"></div>
<div id="widget_disk_partion"></div>

服务器信息
这个小部件向我们显示信息:Linux 内核、CPU 架构、正常运行时间、IP 地址。我们这里不需要图表,一个简单的数据表就可以完成这项工作。调用该类是Server。这是 widget/server.php
的第一个内容<?php
namespace AX\StatBoard\Widget;
use DateTime;
class Server implements Provider {
function __construct() {
}
public function get_title() {
return "Server Info";
}
/**
* Return server info: OS, Kernel, Uptime, and hostname
* @return array with 3 metric:
* * hostname
* * os
* * uptime
*/
function get_metric() {
$server = array();
$server['hostname'] = `hostname`;
$server['os'] = `uname -sr`;
$server['core'] = `grep -c ^processor /proc/cpuinfo`;
$total_uptime_sec = time() - `cut -d. -f1 /proc/uptime`;
$now = new DateTime("now");
$server['uptime'] = $now->diff(new DateTime("@$total_uptime_sec"))->format('%a days, %h hours, %i minutes and %s seconds');
// Get the external ip with ifconfig.me, a website that show you ip address in plaintext
// when sending request with curl header
$server['ip'] = `curl ifconfig.me`;
$server['ram'] = `free -m | grep Mem | awk '{print $2}'`;
$server['cpu'] =`cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "model name" | awk '{print $4,$5,$6,$7}'`;
return $server;
}
}
主机名
显示您的服务器主机名。
名称-sr
显示Linux内核信息:
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ uname -sr Linux 2.6.32-358.23.2.el6.x86_64
grep -c ^处理器/proc/cpuinfo
-c 开关打印输入字符串中匹配行的计数。 /proc/cpuinfo 包含处理器信息。我们 grep 它并计算文字处理器的出现次数。这是我的 32 核结果。
$ grep -c ^processor /proc/cpuinfo 32
剪切-d。 -f1 /proc/uptime
此命令显示服务器已启动并运行的秒数。我们将秒数转换为“x 天 y 小时 z 分钟”的格式,以使其更加用户友好。
使用 DateTime::diff 我们可以轻松实现这一点。我们创建一个带有当前时间戳的 DateTime 对象,另一个带有时间戳的对象是当前时间戳减去正常运行时间的秒数。然后使用 format 方法将其格式化为人类友好的字符串。
这是我的结果,正常运行时间为 26194091 秒。
$ cut -d. -f1 /proc/uptime 26194091
卷曲 ifconfig.me
ifconfig.me 是一项在浏览器内直接访问时显示您的 IP 地址的服务。如果您使用 curl 向其发送请求,它将以单个字符串形式返回您的 IP 地址。
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ curl ifconfig.me 76.102.253.237
CPU型号
如上所述,/proc/cpuinfo存储了CPU信息。我们可以从中提取CPU型号。例如:[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep "model name" | awk '{print $4,$5,$6,$7}'
Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4250U CPU
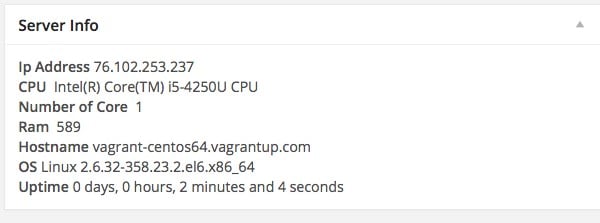
public function get_content() {
$server = $this->get_metric();
echo <<<EOD
<strong>Ip Address</strong> {$server['ip']}<br>
<strong>CPU</strong> {$server['cpu']}<br>
<strong>Number of Core</strong> {$server['core']}<br>
<strong>Ram</strong> {$server['ram']}<br>
<strong>Hostname</strong> {$server['hostname']}<br>
<strong>OS</strong> {$server['os']}<br>
<strong>Uptime</strong> {$server['uptime']}<br>
EOD;
}
处理器
监控我们的处理器是其中之一我们可以展示的最重要的东西。我们想知道某个特定进程正在使用多少 CPU 和/或消耗了多少内存。我们将我们的类称为 Process,首先从 get_title 和 get_metric 开始。我将在代码后面解释 get_metric 的更多细节:<?php
namespace AX\StatBoard\Widget;
class Process implements Provider {
public function get_title() {
return "Processes";
}
/**
* Return server info: OS, Kernel, Uptime, and hostname
* @return array with 3 metric:
* * hostname
* * os
* * uptime
*/
function get_metric() {
$processes = array();
$output = `ps -eo pcpu,pmem,pid,user,args,time,start | grep -v '\[' | sort -k 1 -r | head -30 | awk '{print $4,$3,$1,$2,$7,$6,$5}'`;
$output = explode("\n", $output);
if (!is_array($output) || count($output)<2) {
return false;
}
array_shift($output);
foreach ($output as $line) {
//$line = preg_split('/\s+/', $line);
$line = explode(' ', $line);
if (count($line)<6) {
continue;
}
//var_dump($line);
//echo count($line);
if (empty($processes[$line[6]])) {
$processes[$line[6]] = array_combine(array('user', 'pid', '%cpu', '%mem','start','time', 'command'), $line);
} else {
$processes[$line[6]]['%cpu'] += $line[2];
$processes[$line[6]]['%mem'] += $line[3];
}
}
return $processes;
}
}
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ ps -eo pcpu,pmem,pid,user,args,time,start %CPU %MEM PID USER COMMAND TIME STARTED 0.0 0.2 1 root /sbin/init 00:00:00 06:50:39 0.0 0.0 2 root [kthreadd] 00:00:00 06:50:39 0.0 0.0 3 root [migration/0] 00:00:00 06:50:39
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ ps -eo pcpu,pmem,pid,user,args,time,start | grep -v '\[' %CPU %MEM PID USER COMMAND TIME STARTED 0.0 0.2 1 root /sbin/init 00:00:00 06:50:39 0.0 0.1 292 root /sbin/udevd -d 00:00:00 06:50:41 0.0 0.1 811 root /sbin/dhclient -H vagrant-c 00:00:00 06:50:48 0.0 0.2 948 root /sbin/rsyslogd -i /var/run/ 00:00:00 06:50:50 0.0 0.1 966 rpc rpcbind 00:00:00 06:50:50 0.0 0.2 984 rpcuser rpc.statd 00:00:00 06:50:50 0.0 0.0 1011 root rpc.idmapd 00:00:00 06:50:51 0.0 0.2 1073 root /usr/sbin/VBoxService 00:00:00 06:50:51
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ ps -eo pcpu,pmem,pid,user,args,time,start | grep -v '\[' | sort -k 1 | head -30 | awk '{print $4,$3,$1,$2,$7,$6,$5}'
root 1151 0.0 0.0 00:00:00 -d /sbin/udevd
root 1152 0.0 0.0 00:00:00 -d /sbin/udevd
root 292 0.0 0.0 00:00:00 -d /sbin/udevd
root 811 0.0 0.0 vagrant-c -H /sbin/dhclient
root 1 0.0 0.1 06:50:39 00:00:00 /sbin/init
root 2153 0.0 0.1 -q -1 /sbin/dhclient
root 3642 0.0 0.1 00:00:00 -s /usr/sbin/anacron
vagrant 3808 0.0 0.1 pcpu,pmem,pid,user,a -eo ps
vagrant 3810 0.0 0.1 1 -k sort
vagrant 3811 0.0 0.1 00:00:00 -30 head
vagrant 3812 0.0 0.1 $4,$3,$1,$2,$7,$ {print awk
root 948 0.0 0.1 /var/run/ -i /sbin/rsyslogd
rpc 966 0.0 0.1 06:50:50 00:00:00 rpcbind
root 1073 0.0 0.2 06:50:51 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/VBoxService
root 1105 0.0 0.2 06:50:51 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/sshd
root 1121 0.0 0.2 06:50:52 00:00:00 crond
rpcuser 984 0.0 0.2 06:50:50 00:00:00 rpc.statd
496 1088 0.0 0.3 -p -d memcached
vagrant 3544 0.0 0.3 00:00:00 vagrant@pts/0 sshd:
vagrant 3545 0.0 0.3 06:59:27 00:00:00 -bash
root 1113 0.0 1.7 06:50:52 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 1157 0.0 4.2 06:50:53 00:00:01 /usr/sbin/httpd
apache 3438 0.0 4.2 06:55:39 00:00:01 /usr/sbin/httpd
<?php
//...
// inside get_content
foreach ( $output as $line ) {
//$line = preg_split( '/\s+/', $line );
$line = explode( ' ', $line );
if ( 6 > count( $line ) ) {
continue;
}
if ( empty( $processes[ $line[6] ] ) ) {
$processes[ $line[6]] = array_combine( array( 'user', 'pid', '%cpu', '%mem','start','time', 'command' ), $line );
} else {
$processes[ $line[6] ]['%cpu'] += $line[2];
$processes[ $line[6] ]['%mem'] += $line[3];
}
}
//...
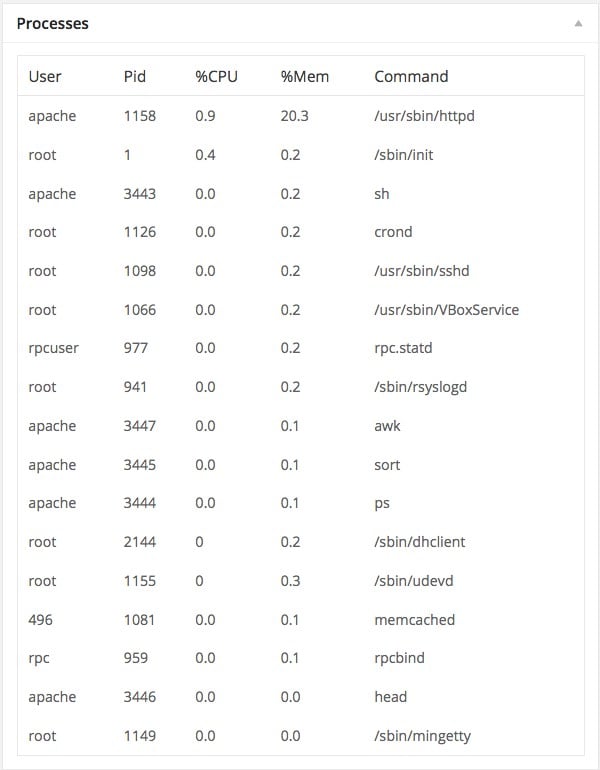
public function get_content() {
$processes = $this->get_metric();
$html = '<table class="wp-list-table widefat"><thead><tr>
<th>User</th>
<th>Pid</th>
<th>%CPU</th>
<th>%Mem</th>
<th>Command</th>
</tr></thead><tbody>';
foreach ($processes as $process) {
$html .= "<tr>
<td>{$process['user']}</td>
<td>{$process['pid']}</td>
<td>{$process['%cpu']}</td>
<td>{$process['%mem']}</td>
<td>{$process['command']}</td>
</tr>";
}
$html .= '</tbody></table>';
echo $html;
}
平均负载
Linux 有一个命令可以显示过去一分钟、五分钟和 15 分钟内 CPU 和 IO 的平均负载。让我们把它压缩成一个小部件。称之为 Cpuload,并创建我们的 widget/cpuload.php
<?php
namespace AX\StatBoard\Widget;
class Cpuload implements Provider {
function __construct() {
}
public function get_title() {
return "CPU Load";
}
function get_metric() { $number_of_core = intval(`/bin/grep -c processor /proc/cpuinfo`); $loadAvg = `cat /proc/loadavg | /usr/bin/awk '{print $1,$2,$3}'`; $loadAvg = explode(' ', $loadAvg); if ($loadAvg <3) { return false; } $loadTimes = array('1 min', '5 mins', '15 mins'); return array_map( function ($loadtime, $value, $number_of_core) { return array($loadtime, round($value * 100 / $number_of_core, 2), $value); }, $loadTimes, $loadAvg, array_fill(0, 3, $number_of_core) ); }
}
部分对此进行了介绍。
~ cat /proc/loadavg
0.01 0.04 0.05 1/217 16089
~ cat /proc/loadavg | awk '{print $1, $2, $3}'
0.01 0.04 0.05
public function get_content() {
$metrics = $this->get_metric();
if ( ! $metrics ) {
return false;
}
// see https://google-developers.appspot.com/chart/interactive/docs/gallery/barchart#Data_Format for more detai of format
$data = array( array( 'Duration', '% Load' ) );
foreach ( $metrics as $key=>$metric ) {
array_push( $data, array( $metric[0], $metric[1] ) );
}
$data = json_encode( $data );
echo <<<EOD
<div id="avg_load"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
google.load("visualization", "1", {packages:["corechart"]});
google.setOnLoadCallback(drawChart);
function drawChart() {
var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable($data);
var options = {
hAxis: {
titleTextStyle: {color: 'red'},
minValue:0,
maxValue:100
}
};
var chart = new google.visualization.BarChart(document.getElementById('avg_load'));
chart.draw(data, options);
}
</script>
EOD;
}
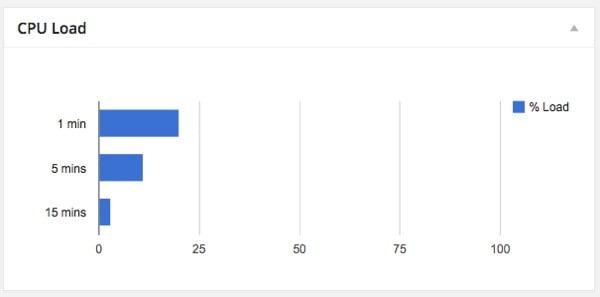
[ ["Duration","% Load"], ["1 min",20], ["5 mins",11], ["15 mins",3]]
以太网接口
我们要处理的下一个小部件是以太网接口。某些服务器可以有多个以太网接口,并为其分配不同的 IP 地址。
看到这些信息非常有用。我们将这个类称为 Ethernet,从 widget/ethernet.php 的基本内容开始。
<?php
/**
* Adopt from https://github.com/afaqurk/linux-dash/blob/master/sh/ip.php
*
*/
namespace AX\StatBoard\Widget;
class Ethernet implements Provider {
function __construct() {
}
public function get_title() {
return "Ethernet";
}
function get_metric() {
$ethernet = array();
$output = shell_exec("ip -oneline link show | awk '{print $2}' | sed 's/://'");
if (!$output) { // It didn't work with "ip" , so we do it with ifconfig
$output = shell_exec(
'ifconfig | /bin/grep -B1 "inet addr" | /usr/bin/awk \'' .
'{ if ( $1 == "inet" ) { print $2 }' .
'else if ( $2 == "Link" ) { printf "%s:",$1 } }\' | /usr/bin/awk' .
' -F: \'{ print $1","$3 }\''
);
$output = trim($output, " \n");
$output = `ifconfig | grep "Link encap" | awk '{ print $1 }'`;
$interfaces = explode("\n", $output);
$output = `ifconfiga | grep "inet addr" | awk '{ print $2 }' | sed 's/addr://'`;
$addreses = explode("\n", $output);
$output = trim($output, " \n");
return array_combine($interfaces, $addreses);
}
$output = trim($output, " \n");
$interfaces = explode("\n", $output);
$addreses = array();
foreach ($interfaces as $interface) {
$output = shell_exec("ip -oneline -family inet addr show $interface | awk '{print $4}' | cut -d'/' -f1");
$addreses[] = $output;
}
return array_combine($interfaces, $addreses);
}
}
$output = shell_exec("ip -oneline link show | awk '{print $2}' | sed 's/://'");
使用 IP 实用程序
带有 ip 命令和 -oneline 将仅在一行中显示输出,其中 link 和 show 将列出所有设备。我们使用 awk 获取第二列,其中包含设备名称;但是它包含 : 字符。我们使用 sed 将 : 替换为空字符串。
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ip -oneline link show
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN \ link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000\ link/ether 08:00:27:08:c2:e4 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000\ link/ether 08:00:27:eb:11:e4 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ip -oneline link show | awk '{print $2}'
lo:
eth0:
eth1:
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ip -oneline link show | awk '{print $2}' | sed 's/://'
lo
eth0
eth1
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$
$output = trim($output, " \n");
$interfaces = explode("\n", $output);
$addreses = array();
foreach ($interfaces as $interface) {
$output = shell_exec("ip -oneline -family inet addr show $interface | awk '{print $4}' | cut -d'/' -f1");
$addreses[] = $output;
}
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ip -oneline -family inet addr show eth1
3: eth1 inet 192.168.1.111/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global eth1
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ip -oneline -family inet addr show eth1 | awk '{print $4}'
192.168.1.111/24
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ip -oneline -family inet addr show eth1 | awk '{print $4}' | cut -d'/' -f1
192.168.1.111
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$
return array_combine($interfaces, $addreses);
使用 ifconfig 的服务器
在 ifconfig 的情况下,ip 的 shell_exec 将返回 false。在这种情况下,我们改为运行 ifconfig。 if (!$output) { // It didn't work with "ip" , so we do it with ifconfig
$output = `ifconfig | grep "Link encap" | awk '{ print $1 }'`;
$interfaces = explode("\n", $output);
$output = `ifconfig | grep "inet addr" | awk '{ print $2 }' | sed 's/addr://'`;
$addreses = explode("\n", $output);
$output = trim($output, " \n");
return array_combine($interfaces, $addreses);
}
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:08:C2:E4
inet addr:10.0.2.15 Bcast:10.0.2.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe08:c2e4/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:4230 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:2575 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:444488 (434.0 KiB) TX bytes:2288676 (2.1 MiB)
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:EB:11:E4
inet addr:192.168.1.111 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:feeb:11e4/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:4470 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:2449 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:1689803 (1.6 MiB) TX bytes:271675 (265.3 KiB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:264 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:264 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:15840 (15.4 KiB) TX bytes:15840 (15.4 KiB)
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ifconfig | grep "Link encap"
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:08:C2:E4
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:EB:11:E4
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ifconfig | grep "Link encap" | awk '{ print $1 }'
eth0
eth1
lo
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ifconfig | grep "inet addr"
inet addr:10.0.2.15 Bcast:10.0.2.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet addr:192.168.1.111 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ifconfig | grep "inet addr" | awk '{ print $2 }'
addr:10.0.2.15
addr:192.168.1.111
addr:127.0.0.1
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ ifconfig | grep "inet addr" | awk '{ print $2 }' | sed 's/addr://'
10.0.2.15
192.168.1.111
127.0.0.1
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$
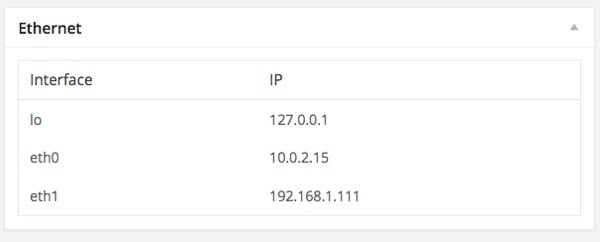
public function get_content() {
$interfaces = $this->get_metric();
$html = '<table class="wp-list-table widefat"><thead><tr>
<th>Interface</th>
<th>IP</th>
</tr></thead><tbody>';
foreach ( $interfaces as $interface => $ip ) {
$html .= "<tr>
<td>{$interface}</td>
<td>{$ip}</td>
</tr>";
}
$html .= '</tbody></table>';
echo $html;
}
网络流量
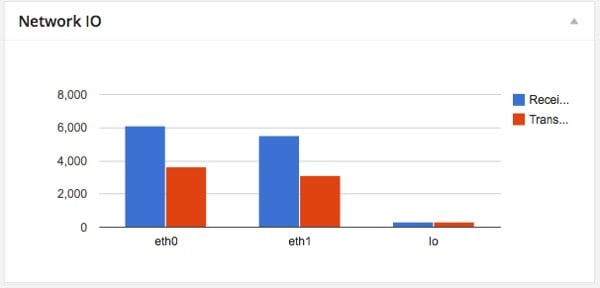
网络流量或网络 IO 显示通过计算机网络传输包的状态。该信息是从 netstat 中提取的。
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ netstat -i Kernel Interface table Iface MTU Met RX-OK RX-ERR RX-DRP RX-OVR TX-OK TX-ERR TX-DRP TX-OVR Flg eth0 1500 0 4828 0 0 0 2933 0 0 0 BMRU eth1 1500 0 4806 0 0 0 2679 0 0 0 BMRU lo 16436 0 276 0 0 0 276 0 0 0 LRU
<?php
/**
* Adopt from https://github.com/afaqurk/linux-dash/blob/master/sh/ip.php
*
*/
namespace AX\StatBoard\Widget;
class Networkio implements Provider {
function __construct() {
}
public function get_title() {
return "Network IO";
}
function get_metric() { $ethernet = array(); $output = `netstat -i | grep -v -E '(Iface|Interface)' | awk '{print $1","$4","$8}'`; $lines = explode("\n", $output); foreach ($lines as $line) { $line = explode(',', $line); if (count($line)<3) { continue; } $ethernet[] = array($line[0], intval($line[1]), intval($line[2])); } return $ethernet; }}
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ netstat -i
Kernel Interface table
Iface MTU Met RX-OK RX-ERR RX-DRP RX-OVR TX-OK TX-ERR TX-DRP TX-OVR Flg
eth0 1500 0 5727 0 0 0 3400 0 0 0 BMRU
eth1 1500 0 5004 0 0 0 2797 0 0 0 BMRU
lo 16436 0 292 0 0 0 292 0 0 0 LRU
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ netstat -i | grep -v -E '(Iface|Interface)'
eth0 1500 0 5736 0 0 0 3405 0 0 0 BMRU
eth1 1500 0 5004 0 0 0 2797 0 0 0 BMRU
lo 16436 0 292 0 0 0 292 0 0 0 LRU
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ netstat -i | grep -v -E '(Iface|Interface)' | awk '{print $1","$4","$8}'
eth0,5760,3420
eth1,5004,2797
lo,292,292
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$
在我们的get_metric中,我们将结果逐行拆分到一个数组中。因为每一行都包含用逗号分隔的数据,所以它们被再次分割成一个数组。
public function get_content() {
$interfaces = $this->get_metric();
$data = array_merge(array(array('Interface', 'Receive(package)', 'Transfer(package)')), $interfaces);
$data = json_encode($data);
echo <<<EOD
<div id="nio_chart"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
google.setOnLoadCallback(function () {
var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable({$data});
var options = {
};
var chart = new google.visualization.ColumnChart(document.getElementById('nio_chart'));
chart.draw(data, options);
})
</script>
EOD;
}
输入/输出统计
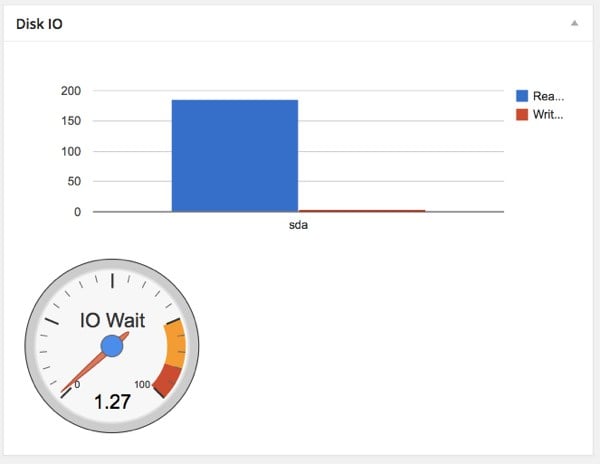
现在,我们处理 io stat。 IO 表示输入/输出。我们将了解每秒执行多少次读/写操作。我们还处理 io_wait。 IO等待是CPU空闲等待从硬盘读取结果的时间。
比如你正在读取MySQL数据,CPU会空闲下来等待结果。 io wait 按1秒或1000毫秒计算。如果您的代码需要 100 毫秒从硬盘读取数据,则 io_wait 为 100/1000 = 10%。 IO 等待越少,系统性能越好。
为了继续执行此操作,请确保系统上有 sysstat 软件包。
- 对于 Arch Linux,使用 pacman -S sysstat 安装
- 对于 Debian/Ubuntu,您可以使用 apt-get install sysstat 获取它们
- 对于 Fedora/Centos,您可以使用 yum install sysstat
- 对于其他发行版,:请使用您的发行版包管理器进行安装
安装完成后,让我们评估一下我们将使用的一些命令。首先是第一件事:
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 sbin]$ iostat
Linux 2.6.32-358.23.2.el6.x86_64 (vagrant-centos64.vagrantup.com) 04/27/2014 _x86_64_ (1 CPU)
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
0.05 0.00 0.25 0.04 0.00 99.66
Device: tps Blk_read/s Blk_wrtn/s Blk_read Blk_wrtn
sda 0.18 7.62 1.04 157826 21584
[vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$ cat /sys/block/sda/queue/physical_block_size 512 [vagrant@vagrant-centos64 ~]$
有了上面的基本知识,让我们在 widget/iostat.php 中创建我们的类 Iostat 。
<?php
namespace AX\StatBoard\Widget;
class Iostat implements Provider {
function __construct() {
}
public function get_title() {
return "Disk IO";
}
/**
* Make sure we install package sysstat
* yum install sysstat
* or apt-get install sysstat
*
* Return IO Stat information. CPU waiting time, disk read/write
*
*/
function get_metric() {
$metric = array();
$output = `iostat`;
$number_of_core = intval(`/bin/grep -c processor /proc/cpuinfo`);
$lines = explode("\n", $output);
//We should have more than 4 lines
if (!is_array($lines) || sizeof($lines)<4) {
return false;
}
$avg_cpu = preg_split("/\s+/", $lines[3]);
$metric['cpu'] = array(
'user' => floatval($avg_cpu[0]) * $number_of_core,
'system' => floatval($avg_cpu[2]) * $number_of_core,
'io_wait' => floatval($avg_cpu[3]) * $number_of_core,
'other' => 100 - ($avg_cpu[0] + $avg_cpu[2] + $avg_cpu[3])
);
if (sizeof($lines) >=7) {
for ($i=6,$l = sizeof($lines);$i<$l; $i++) {
$line = preg_split("/\s+/", $lines[$i]);
if (!is_array($line) || sizeof($line)<5) {
continue;
}
// Calculate block size
$block_size = shell_exec("cat /sys/block/{$lines[1]}/queue/physical_block_size");
$metric['disk'][$line[0]] = array(
'read' => floatval($line[2]) * $block_size / 1024,
'write' => floatval($line[3]) * $block_size / 1024,
);
}
}
return $metric;
}
}
public function get_content() {
$metric = $this->get_metric();
$disk_io = array(
array('Disk', 'Read(MB)', 'Write(MB)'),
);
foreach ($metric['disk'] as $disk=>$stat) {
$disk_io[] = array($disk, $stat['read'], $stat['write']);
}
$disk_io = json_encode($disk_io);
$cpu_io = json_encode(array(
array('CPU Time', 'Percent'),
array('IO Wait', $metric['cpu']['io_wait']),
));
echo <<<EOD
<div id="widget_disk_io"></div>
<div id="widget_cpu_io_wait"></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
google.load('visualization', '1', {packages:['gauge']});
google.setOnLoadCallback(function () {
var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable({$cpu_io});
var goptions = {
redFrom: 80, redTo: 100,
yellowFrom:50, yellowTo: 80,
minorTicks: 5
};
var chart = new google.visualization.Gauge(document.getElementById('widget_cpu_io_wait'));
chart.draw(data, goptions);
var data2 = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable({$disk_io});
var chart2 = new google.visualization.ColumnChart(document.getElementById('widget_disk_io'));
chart2.draw(data2, {});
})
</script>
EOD;
}
将Transforming a WordPress Server Dashboard into a Widget的详细内容,更多请关注红帽云邮其它相关文章!

这里不仅为大家提供了WPS Office安装包,还有office/word/excel/ppt/wps的零基础入门到精通超全教程,你想学的和不懂的,这里都有!感兴趣的小伙伴快来保存学习吧!

-
2024-07-24 18:20:14
-
2024-07-24 18:14:22
-
2024-07-24 18:07:44
-
2024-07-24 18:05:05
-
2024-07-24 18:04:21
-
2024-07-24 18:01:00
-
2024-07-24 17:55:29
-
2024-07-24 17:51:14
-
2024-07-24 17:50:25
-
2024-07-24 17:49:22
 邮件群发-邮件群发软件|邮件批量发送工具|群发邮件平台|批量邮箱发送系统公司
邮件群发-邮件群发软件|邮件批量发送工具|群发邮件平台|批量邮箱发送系统公司

















